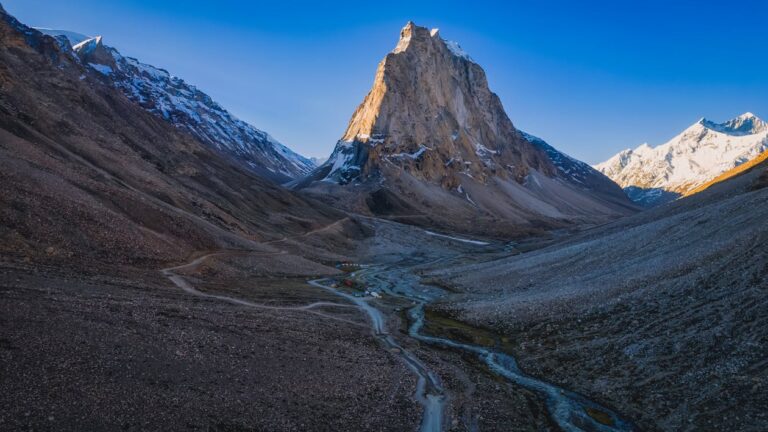
The Ultimate Ladakh Travel Guide
(2025)

Ladakh is the dream destination of travellers all around the globe.
Anyone who is interested in experiential travel, scenic landscapes, photogenic glacial lakes, peaceful monasteries & understands the importance of travelling responsibly deserves a Trip to Ladakh.
The Ultimate Ladakh Travel Guide is our attempt at helping the travellers understand Ladakh better & prepare for this amazing destination.
Table of Contents
ToggleBrief History of Ladakh!
According to various Texts related to Ladakh & Tibetan History Maryul (meaning lowerland in Tibetan) was the ancient name of Ladakh until the 16th Century. With time it got renamed to Ladakh as we know it today.
– “La” means Mountain Pass & “Dakh” means Country. Hence the word Ladakh means the Country of High Passes.
Ancient Period:
- Early Settlements: Ladakh’s history dates back to around 9000 B.C. with evidence of early human settlements. It was part of the Kushan Empire in the 1st century, which played a significant role in the spread of Buddhism.
- Buddhist Influence: The region saw a significant influx of Buddhism, with many monasteries established. These monasteries, such as Hemis, Thiksey, and Alchi, are now major tourist attractions, showcasing ancient art and architecture.
Medieval Period:
- Tibetan Rule: In the 7th century, Ladakh came under Tibetan influence. This period marked the beginning of the region’s importance as a part of the Silk Route, facilitating trade between Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent.
- Kingdom of Ladakh: The kingdom was founded in the 10th century and extended from Ruthog to the Kashmir. The Namgyal dynasty, which ruled Ladakh, built several palaces and forts, including the famous Leh Palace, which is a major tourist attraction today.
Modern Period:
- 19th Century Onwards: In the 19th century, Ladakh became part of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. This period saw the construction of roads and other infrastructure, making the region more accessible to travelers.
- Union Territory: On October 31, 2019, Ladakh was established as a union territory of India. This political change has brought more focus on developing tourism infrastructure and promoting Ladakh as a prime travel destination.
Ladakh’s unique blend of history, culture, and natural beauty makes it a must-visit destination for travelers seeking both adventure and tranquility.
Basic Geography of Ladakh
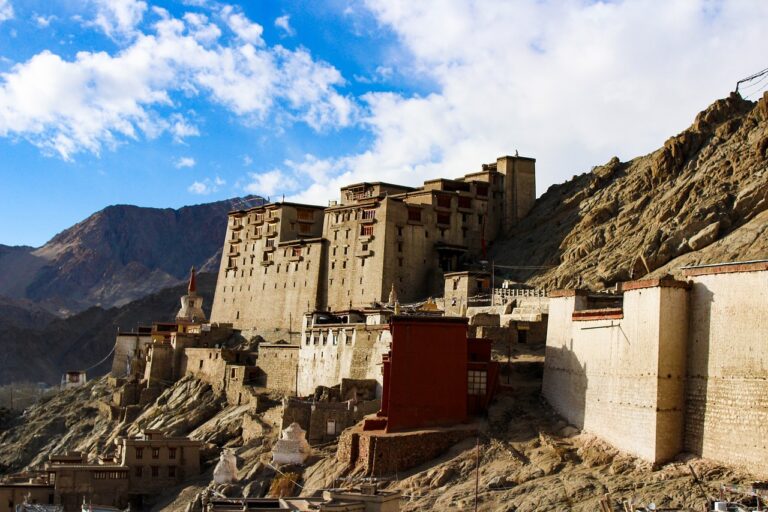

Ladakh, the northern most region of India is situated at an altitude range of 3000 – 8000 meters approx. It is home to some of the world’s highest mountain passes & lakes. Here is an in depth look at what makes Ladakh, a unique destination for travellers and an important region for India.
1. Location and Borders
Ladakh lies in northern India, bordered by Tibet in the east, Himachal Pradesh to the south, and Jammu and Kashmir to the west. It shares international borders with Pakistan and China, making it strategically significant.
2. Topography
Known for its rugged, high-altitude desert landscape, Ladakh is cradled by the Himalayas and the Karakoram mountain ranges. With elevations ranging from 9,000 to 25,000 feet, it’s among the world’s highest inhabited regions, famous for towering peaks, steep cliffs, and expansive valleys.
3. Major Rivers in Ladakh
The Indus River, Ladakh’s primary water source, flows from Tibet, supporting life in this arid region. Other rivers, including the Zanskar River and Shyok River, carve out fertile valleys and provide water for the limited agriculture in Ladakh.
4. Climate in Ladakh
Ladakh’s climate is extreme, with winter temperatures dropping below -20°C (-4°F) and summer highs reaching up to 25°C (77°F). The region sits in a rain shadow, receiving minimal precipitation, resulting in a cold desert environment that limits vegetation to only the hardiest shrubs and grasses.
5. Flora and Fauna
Despite the harsh climate, Ladakh boasts diverse wildlife. Iconic species include the snow leopard, ibex, yak, and blue sheep. Vegetation is sparse, mainly hardy shrubs and grasses found in river valleys and lower elevations, giving Ladakh a unique, stark beauty.
6. Glaciers and Lakes
Ladakh is home to significant glaciers, including the Siachen Glacier, one of the world’s longest glaciers outside the polar regions. The area’s high-altitude lakes, like Pangong Tso, Tso Moriri, and Tso Kar, are famous for their pristine, turquoise waters, attracting travelers and photographers alike.
7. Union Territory and Districts
After 2019, Ladakh became a Union Territory with two main districts, Leh and Kargil, and a total of seven administrative districts. The new status underscores Ladakh’s importance as a strategic and cultural region within India.
8. Strategic Significance of Ladakh
Ladakh’s location between India, China, and Pakistan makes it geopolitically vital. As a result, the Indian government has invested in defense infrastructure and development in the area, ensuring the safety and security of its borders.
With its extreme landscapes, distinct culture, and breathtaking beauty, Ladakh is a top travel destination. This geographically significant region appeals to adventure travelers, nature lovers, and culture enthusiasts, all drawn by Ladakh’s unique charm and importance in India.
Why Ladakh Should Be Your Next Adventure: 10 Irresistible Reasons to Visit
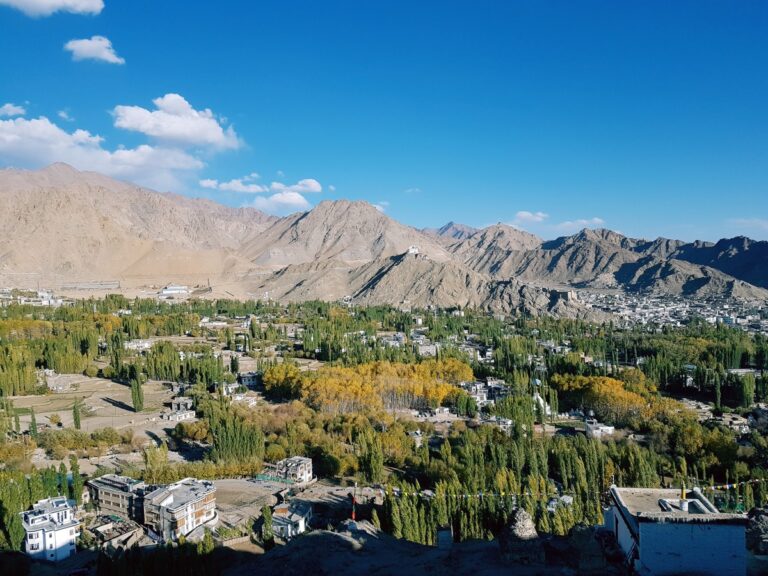

Ladakh is a magical land of contrasts, where rugged mountains meet peaceful monasteries, and adventure blends seamlessly with spirituality. If you’re looking for a travel destination that promises unforgettable experiences, here’s why Ladakh deserves the top spot on your travel bucket list:
-
Breathtaking Landscapes Like No Other:
Imagine standing in the shadow of towering snow-capped peaks, gazing at crystal-clear glacial lakes, or wandering through vast deserts.
From the surreal blue of Tso Moriri & Pangong Lake to the cold desert terrain of Nubra Valley, and moon like terrain of The Moonland – Lamayuru Ladakh’s diverse scenery will leave you speechless and your camera full. -
Rich Culture & Timeless Heritage:
Ladakh is more than just a feast for the eyes; it’s a place steeped in history and culture.
Ancient monasteries like Hemis, Thiksey, and Alchi transport you back in time, offering a glimpse into the region’s Tibetan Buddhist traditions. Attend a vibrant festival or witness prayer ceremonies—these experiences will touch your soul and deepen your appreciation for Ladakh’s spiritual roots. -
A Playground for Adventure Seekers:
Whether you’re trekking across dramatic mountain trails, rafting down the mighty Indus River, or navigating rugged paths on a mountain bike, Ladakh is an adventurer’s dream. With challenges that match the breathtaking scenery, every turn offers new thrills.
-
A Tranquil Escape From the Hustle:
In Ladakh, the air feels different—crisp, pure, and peaceful. The sparsely populated region offers an unmatched sense of serenity. Disconnect from the chaos of modern life and reconnect with nature in its purest form. The quiet valleys and starry nights will soothe your soul.
-
Wildlife You Won’t Find Anywhere Else:
For nature lovers, Ladakh’s remote wilderness is home to rare and elusive creatures. Spot snow leopards, Himalayan ibex, and Tibetan antelope in their natural habitats, or enjoy birdwatching as you encounter black-necked cranes and golden eagles soaring above the valleys.
-
Flavors You’ll Crave Long After You Leave:
Ladakhi cuisine is as unique as its landscape. Warm up with a bowl of delicious thukpa (noodle soup), savor the irresistible momos (dumplings), along with a lot of local options.. These authentic flavors carry the warmth and heart of Ladakhi culture and will leave your taste buds wanting more.
-
Welcoming Locals Who Feel Like Family:
The people of Ladakh are as warm as the sunlit valleys they call home. Their genuine hospitality and eagerness to share their traditions make every interaction a memorable one. Whether you’re invited to a local home for tea or engaging in casual conversation, you’ll quickly feel like part of the community.
-
Discover the Road Less Traveled:
Ladakh offers a rare opportunity to explore a destination untouched by mass tourism. Roam remote villages, trek through landscapes where few have set foot, and discover hidden gems at every turn. It’s a true off-the-beaten-path adventure that invites you to experience authenticity.
-
Festivals Bursting With Color and Life:
Ladakh’s festivals are a vibrant spectacle of music, dance, and devotion. The Hemis Tsechu, Stok Guru Tsechu, and Sindhu Darshan are just a few of the cultural events where you can witness masked dances, vibrant costumes, and centuries-old traditions, all while being part of the lively celebrations.
-
A Journey of Self-Discovery:
Ladakh isn’t just a destination—it’s a journey that challenges and transforms you. The raw beauty, extreme weather, and demanding treks offer a chance to test your limits and find inner strength. Amidst the vast, awe-inspiring landscapes, you might just discover a new side of yourself.
Administrative Structure of Ladakh
Ladakh, known for its breathtaking landscapes and unique cultural heritage, has recently been reorganized into seven districts to enhance governance and bring essential services closer to its residents. This guide delves into each of these districts, providing insights into their significance, key attractions, and what makes them stand out.

1. Leh:
Leh is the administrative capital and largest district of Ladakh, attracting most travelers and offering access to various parts of the region. Known for its magnificent monasteries like Thiksey and Hemis and the iconic Leh Palace.
Key Attractions:
- Leh Palace
- Shanti Stupa
- Thiksey Monastery
- Hemis Gompa
- Leh Market
2. Kargil
Kargil, famous for its historical significance in the 1999 Kargil War, is the second-largest district in Ladakh. It connects Leh and Srinagar and serves as a cultural blend of Tibetan and Kashmiri traditions. Kargil is also the entryway to Zanskar Valley, a breathtaking and remote area of Ladakh.
Key Attractions:
- Drass War Memorial
- Mulbekh Monastery
- Suru Valley
- Zanskar Valley
3. Zanskar
A newly formed district, Zanskar is among the most remote and less-explored areas of Ladakh. Known for its dramatic landscapes and ancient monasteries, Zanskar offers unparalleled trekking and adventure, including the famous Chadar Trek, where the Zanskar River freezes in winter.
Key Attractions:
- Chadar Trek
- Phugtal Monastery
- Stongdey Monastery
- Zanskar River
4. Drass
Often called the second coldest inhabited place on Earth, Drass is located on the Srinagar-Leh Highway. Known for its extreme climate and role in the Kargil War, it’s a popular stop en route to Leh, offering rugged terrain views.
Key Attractions:
- Drass War Memorial
- Mushkoh Valley
- Trekking to Suru Valley
5. Sham Valley
Sham Valley is known for its lush green landscapes and traditional villages. Home to some of Ladakh’s oldest monasteries, such as Likir and Alchi, Sham Valley is ideal for exploring Ladakh’s cultural heritage and enjoying scenic treks.
Key Attractions:
- Alchi Monastery
- Likir Monastery
- Basgo Palace
- Sham Valley Trek
6. Nubra Valley
Now a district, Nubra Valley is famed for its sand dunes, Bactrian camels, and monasteries like Diskit and Samstanling Gompa. Located north of Leh and accessible via the Khardung La Pass, it offers desert landscapes alongside lush green oases.
Key Attractions:
- Diskit Monastery
- Hunder Sand Dunes
- Turtuk Village
- Panamik Hot Springs
- Yarab Tso Lake
- Siachen War Memorial
7. Changthang
Known for high-altitude plateaus and nomadic tribes, Changthang is a region of stark beauty. This district includes high-altitude lakes like Tso Moriri and Tso Kar, and offers a glimpse into the lifestyle of Ladakhi nomads.
Key Attractions:
- Tso Moriri Lake
- Tso Kar Lake
- Korzok Monastery
- Changpa Nomadic Life
Best Time to Visit Ladakh !
This period is ideal for visiting Ladakh, with pleasant weather and all tourist attractions accessible. The temperatures range from 15°C to 30°C, making it perfect for sightseeing and outdoor activities. During these months, the roads are clear of snow, and the region is buzzing with activity. This is also the best time for trekking in Ladakh and other adventure sports.
Ladakh experiences harsh winters with temperatures dropping well below freezing. However, this is the time to witness Ladakh's stunning winter beauty and partake in winter sports like ice skating and snow trekking. The temperatures can range from -20°C to 10°C. Visiting during the off-season requires preparation for the cold, but the rewards include fewer tourists, pristine landscapes, and unique winter experiences like the Chadar Trek on the frozen Zanskar River.
- June to September: Pleasant days and cool nights, perfect for exploring monasteries, lakes, and valleys. Summer festivals like Hemis Festival also occur during this period.
- October to May: Extremely cold with heavy snowfall, especially in higher regions. However, it's a great time for photographers to capture the snow-clad beauty of Ladakh, and for those seeking solitude and a raw experience of nature.
How to Reach Ladakh?

By Road:
- Manali – Leh Highway: This iconic route, open from June to September, is a favorite among adventure enthusiasts and road trip lovers. The Manali-Leh Highway takes you through some of the most breathtaking landscapes in the world, including the famous Rohtang Pass, Baralacha La, and Tanglang La, one of the highest motorable passes. The journey is challenging, with rugged terrains and high-altitude passes, but the mesmerizing beauty of the landscape makes it all worthwhile. Travelers should be prepared for basic facilities en route, making it essential to plan ahead.
- Srinagar – Leh Highway: The Srinagar-Leh Highway, accessible from May to October, offers a more gradual ascent, making it easier for travelers to acclimatize to the altitude. This route is equally scenic, passing through the lush green Kashmir Valley and the majestic Zojila Pass. Along the way, you can explore significant historical and cultural sites such as the Kargil War Memorial in Drass, the second coldest inhabited place in the world, and several ancient monasteries. This route is ideal for those who wish to combine their journey with a visit to the beautiful Kashmir region.
- Manali – Shinkula – Zanskar Route: For those seeking an off-the-beaten-path adventure, the Manali-Shinkula-Zanskar route is a relatively new and less-traveled option. This route, which offers access to the remote Zanskar Valley, is perfect for travelers who want to experience the raw, untouched beauty of Ladakh. The journey is filled with rugged landscapes, secluded villages, and a sense of solitude that is hard to find elsewhere. The route is open during the summer months, and due to its challenging nature, it is recommended for seasoned travelers looking for an extraordinary adventure.
By Air:
The quickest and most convenient way to reach Ladakh is by air. The Kushok Bakula Rinpochee Airport in Leh is well-connected with regular flights from major Indian cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Srinagar.
The flight to Leh is an experience in itself, offering stunning aerial views of the snow-capped Himalayan peaks. Upon arrival, it is crucial to rest for a day or two to acclimatize to the high altitude, ensuring a comfortable stay in this high-altitude region.
Permits Required for Travel in Ladakh: What You Need to Know
Inner Line Permit (ILP):
For Indian citizens planning to visit protected areas in Ladakh, such as Nubra Valley, Pangong Lake, and Tso Moriri, an Inner Line Permit (ILP) is mandatory. This permit is essential for regulating the movement of travelers in these sensitive regions, ensuring both their safety and the preservation of the area’s cultural and environmental integrity. The ILP allows access to some of the most picturesque and remote areas of Ladakh, making it an essential document for your trip.
Protected Area Permit (PAP):
Foreign nationals traveling to Ladakh need to obtain a Protected Area Permit (PAP) to visit protected regions. The PAP is required for areas like Nubra Valley, Pangong Lake, and Tso Moriri, similar to the ILP for Indian citizens. In certain restricted zones, foreign nationals are required to travel in groups or be accompanied by an authorized travel agent.
This regulation is in place to ensure the safety of travelers and to monitor activities in these strategically sensitive areas. The PAP is crucial for exploring the breathtaking landscapes of Ladakh while adhering to local regulations.
How to Apply for Permits:
Obtaining the necessary permits for Ladakh is a straightforward process. Permits can be applied for online through the official Ladakh government portal – http://lahdclehpermit.in/ or obtained in person at the District Commissioner’s (DC) office in Leh.
To avoid any last-minute delays, it is advisable to apply for the permits well in advance of your travel dates. When applying, ensure you have multiple photocopies of your ID proofs and passport-sized photographs, as these are required during the application process. Once you have your permits, make sure to carry them with you at all times, as they will be checked at various checkpoints along your journey.
Types of Accommodation in Ladakh: Finding Your Perfect Stay

Hotels:
Ladakh offers a wide range of hotel accommodations to suit every budget and preference. From budget-friendly options to luxurious resorts, hotels in Ladakh provide varying levels of comfort and amenities.
Budget hotels offer essential facilities such as clean rooms and basic services, making them ideal for travelers looking to explore Ladakh without overspending.
On the other hand, luxury hotels and resorts in Ladakh provide a more indulgent experience, featuring amenities like spa services, traditional Ladakhi architecture, and breathtaking views of the surrounding Himalayan peaks. Whether you seek simplicity or opulence, there’s a hotel in Ladakh to meet your needs.
Homestays:
For an immersive cultural experience, consider staying in a Ladakhi homestay. Homestays offer the unique opportunity to live with local families, giving you firsthand insight into the Ladakhi way of life. This type of accommodation is not only about finding a place to sleep but also about engaging with the community & enjoying traditional Ladakhi meals.
By choosing a homestay, you support local communities directly and gain a richer understanding of Ladakh’s culture and traditions. It’s an ideal option for travelers looking to experience Ladakh beyond the usual tourist routes.
Camps:
For adventure enthusiasts and nature lovers, camping in Ladakh offers an unparalleled experience. Campsites are available in some of the most scenic locations, such as Pangong Lake, Nubra Valley, and Tso Moriri, allowing you to immerse yourself in Ladakh’s natural beauty. These camps provide comfortable tents equipped with essential amenities like cozy bedding, clean washrooms, and dining facilities.
Staying in a camp gives you the chance to experience the raw beauty of Ladakh up close, with the added thrill of outdoor living. Whether it’s stargazing by the lake or waking up to panoramic mountain views, camping in Ladakh is an experience like no other.
Popular Areas and Locations to Stay in Ladakh: Where to Base Your Adventure
Leh : The Heart of Ladakh
Leh is the central hub of Ladakh and the most popular place to stay for travelers. This bustling town offers a wide range of accommodations, from budget guesthouses to luxury hotels, catering to all types of travelers.
Leh is the perfect starting point for most journeys into Ladakh, providing easy access to all supplies, markets, and cultural sites like the Leh Palace, Shanti Stupa, and various monasteries.
The town is also home to numerous restaurants and shops, making it convenient for travelers to stock up on essentials and enjoy local cuisine. Whether you’re planning day trips or longer excursions, staying in Leh ensures you’re well-connected to the region’s main attractions.

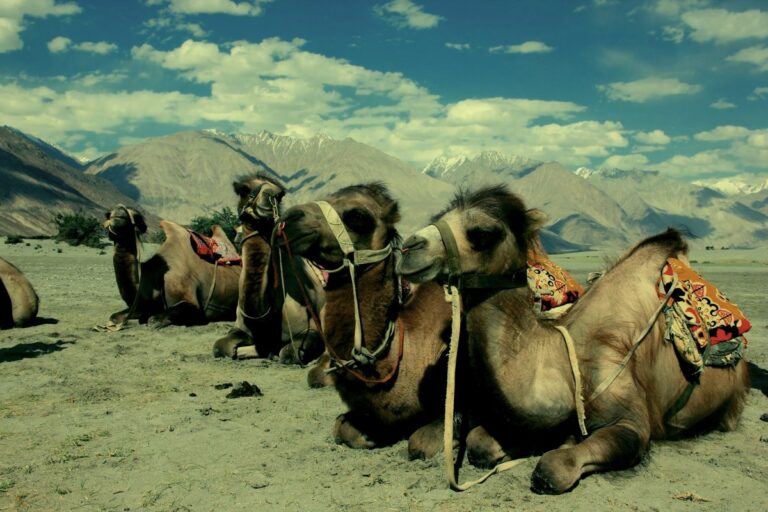
Nubra Valley : The Cold Desert
The name Nubra is derived from Dumra – meaning “The Valley of Flowers” in Tibetan.
Nubra Valley is one of the most enchanting regions in Ladakh, known for its unique landscapes, cultural diversity, and adventure activities.
The valley has some villages popular among travellers. Diskit, famous for its ancient monastery, a beautiful Giant Buddha statue, and mesmerizing view of the valley. Hunder, where you can experience the surreal sand dunes and ride on double-humped Bactrian camels. Turtuk, a remote village near the Indo-Pak border, offers a fascinating glimpse into the region’s Muslim culture and history. Thang, the last village on the Indo – pak border having a good view of the LOC & a village of our neighbouring country.
Accommodation options in Nubra Valley range from guesthouses to luxury camps, allowing you to stay amidst the valley’s breathtaking beauty. Nubra Valley is ideal for travelers looking to experience a mix of nature, culture, and adventure.

Pangong Tso : World’s Highest Saltwater Lake
Pangong Lake is one of Ladakh’s most iconic destinations, known for its crystal-clear waters that change colors throughout the day.
The lake is surrounded by serene and picturesque villages like Spangmik, Man, and Merak, where you can find unique camping experiences.
Staying near Pangong Lake offers an unparalleled opportunity to immerse yourself in the natural beauty of Ladakh. The campsites here provide comfortable tents with basic amenities, allowing you to enjoy the tranquility and stunning views of the lake.
Waking up to the sight of the sun rising over Pangong’s shimmering waters is an experience that shouldn’t be missed.
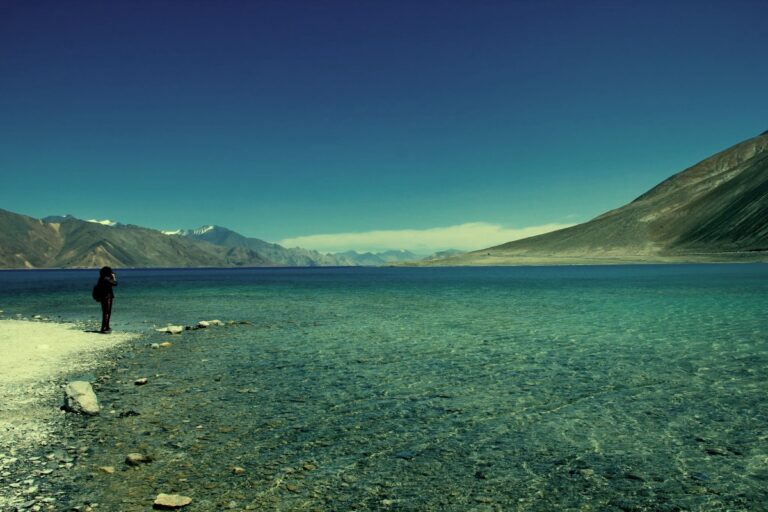

Hanle : Stargazing Heaven
Hanle is a remote and peaceful area that has recently gained popularity, particularly among stargazers and astrophotographers.
Home to one of the world’s highest astronomical observatory, Hanle offers some of the clearest night skies, making it a perfect destination for those interested in astronomy.
The region is also rich in culture, with a small monastery and traditional Ladakhi villages. Accommodation in Hanle is more limited, with options mainly consisting of guesthouses and homestays, but the unique experience of observing the night sky in such a pristine environment makes it well worth the visit.

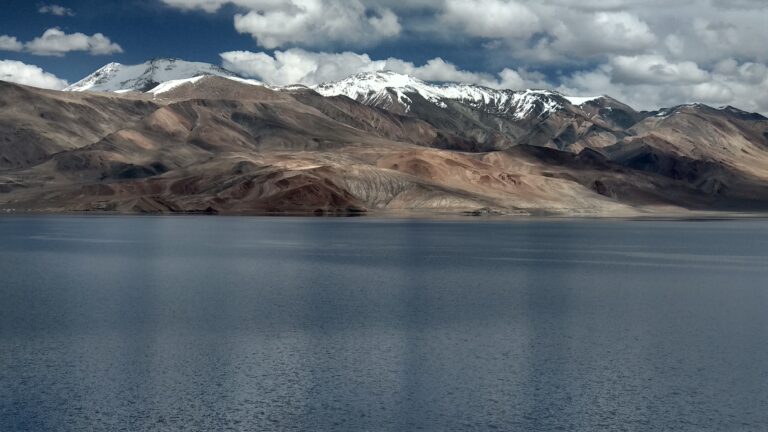
Tso Moriri : Most Beautiful Lake of Ladakh
Tso Moriri, a high-altitude lake located in the Changthang region, offers an off-the-beaten-path experience. Most of the travellers who visit Tso moriri claim it as one of the most beautiful lakes of Ladakh.
Staying in Korzok village or nearby camps provides serene views of the lake and its surrounding mountains. This region is perfect for those seeking peace and opportunities to spot wildlife like migratory birds.

Zanskar : The Hidden Gem
Zanskar Valley is an offbeat destination in Ladakh, renowned for its stunning landscapes and thrilling adventure opportunities. Unlike the more commercialized areas of Ladakh, Zanskar remains largely untouched, offering a more raw and authentic experience.
The Phugtal Monastery & Gombo Rongon (holy mountain) have recently gained a lot of popularity among travellers.
The valley is famous for trekking routes, including the challenging Chadar Trek over the frozen Zanskar River, as well as river rafting and exploring ancient monasteries.
Accommodation in Zanskar is basic, with guesthouses and homestays being the primary options, but the valley’s natural beauty and tranquility make it a haven for adventure enthusiasts and those seeking solitude. A few luxury properties have been recently developed in the area.
Packing Essentials for Ladakh
-
Clothing for Varying Weather Conditions:
Pack layered clothing to adapt to fluctuating temperatures. Include warm jackets, thermal wear, gloves, and beanies for the cold, as well as lighter clothing for the daytime. A good windproof and waterproof jacket is essential.
-
Essential Gear:
Sunglasses, hats, and lip balm to protect against the harsh sun and dry weather. Additionally, carry a sturdy pair of hiking boots, a reusable water bottle, and a backpack for day trips.
-
Medicine & First Aid:
Carry a well-stocked first aid kit, altitude sickness medication, pain relievers, band-aids, antiseptic cream, and any personal medications. Consider including medication for stomach issues as changes in diet and altitude can affect digestion.
Health & Safety Recommendations for Ladakh
Altitude Sickness:
- Symptoms: Headache, nausea, dizziness, and shortness of breath are common symptoms. More severe symptoms include confusion, difficulty walking, and persistent dry cough.
- Prevention: Gradual ascent, staying hydrated, avoiding alcohol, and avoiding strenuous activities for the first 24 hours. Acclimatize properly by spending a couple of days in Leh before venturing to higher altitudes.
- Treatment: Rest, descent to a lower altitude if symptoms worsen, and medication like Diamox (consult a doctor). In severe cases, seek medical attention immediately.
Staying Hydrated & Eating Right:
Drink plenty of water (at least 3-4 liters a day), eat light and frequent meals, and avoid heavy and greasy foods. Include fruits, vegetables, and foods rich in carbohydrates for sustained energy.
Keep a list of emergency contacts, nearest medical facilities, and pharmacies. In Leh, SNM Hospital is the main hospital equipped to handle emergencies.
Sonam Nurboo Memorial Hospital, Leh-Ladakh
Govt. S.N.M. Hospital, Leh-Ladakh,194101
Phone : +911982252012
Getting Around Ladakh : Transportation
Modes of Transportation:
- Rented Bikes: Popular among adventure enthusiasts, offering freedom to explore at your own pace. Ensure you have a valid driving license and are comfortable with high-altitude riding. Rented bikes from outside Ladakh are not allowed. Even for personal bikes, you must have the bike in your own name or have proof of relationship with the owner.
- Cars: Available for hire with or without a driver from Leh. Ideal for families and larger groups. 4×4 vehicles are recommended for tougher terrains. Same policy for cabs/taxi’s is applicable. Taxis / Rented vehicles from outside Ladakh are not allowed.
- Public Transport: Buses and shared taxis are available but less frequent. Public transport is a budget-friendly option but may not cover all remote areas.
Road Conditions & Travel Tips:
- Be prepared for rough and unpredictable road conditions, especially on high passes and remote areas. Landslides and road closures can occur, so always have an alternative plan.
- Carry extra fuel, spare tires, and essential car repair tools. Fuel stations are sparse in remote areas, so fill up whenever possible.
- Check weather and road status before starting your journey. Local authorities and travel agencies provide updates on road conditions and weather forecasts.
- Contact Us for Any Transport Requirements: Assistance with booking bikes, cars, and arranging public transport as per your needs. We provide reliable transport services and ensure that all vehicles are well-maintained for your safety and comfort.
Adventure Activities in Ladakh
- Trekking & Mountaineering – Popular Treks : Snow Leopard Trek in Hemis National Park, Markha Valley Trek, Rumtse to Tso Moriri Trek, Kang Yatse II peak, Chadar Lake Trek, Dzo Jongo Peak Trek.
- River Rafting – Key Locations: Indus River and Zanskar River (with rapids ranging from Grade I to V).
- Mountain Biking – Routes: Manali-Leh Highway, Khardung La Pass to Leh, and Pangong Lake circuits.
- Motorbiking – Routes: Manali to Leh, Leh to Nubra Valley, and Leh to Pangong Lake.
- Camping – Popular Spots: Pangong Lake, Tso Moriri Lake, Nubra Valley, and Zanskar Valley.
- Rock Climbing – Key Locations: Suru Valley and Nubra Valley offer ideal climbing spots with rugged rock faces.
- Paragliding – Popular Sites: Sakti Village & Tungsten Village are the popular spots for paragliding. Both are near Leh & provide panoramic views for paragliding enthusiasts.
- Quad Biking –Best Location: Hunder Sand Dunes in Nubra Valley offers thrilling quad biking experiences on desert dunes.
- Skiing and Snowboarding – Popular Area: Drass in the Kargil district is known for winter sports, especially skiing and snowboarding.
- Ice Hockey – Season: Winter; locations like Leh hold ice hockey tournaments on frozen lakes and ponds.
- Camel Safari – Main Area: Hunder in Nubra Valley, where double-humped Bactrian camel rides are popular.
- Wildlife Safari – Where: Hemis National Park is home to snow leopards, blue sheep, and other high-altitude wildlife.
- Zip Lining – Locations: Stakna near the Leh & Khalsar in Nubra Valley are popular for zip-lining in Ladakh.
- Bird Watching – Best Spots: Shey-Thiksey Marshes, Tso Moriri, Puga-Sumdo Valley, Pangong Lake, known for rare high-altitude birds like the black-necked crane.
Local Festivals and Events of Ladakh

Winter Festivals in Ladakh (December to February)
Ladakh’s winters offer a fascinating mix of snow-covered beauty and vibrant celebrations that warm the cold season.
Losar (Ladakhi New Year)
Approximate Time: Late December
Location: Throughout Ladakh
Highlights: This New Year celebration includes dances, prayers, and offerings, invoking harmony and prosperity.Spituk Gustor Festival
Approximate Time: Early January
Location: Spituk Monastery
Highlights: Cham mask dances performed by monks symbolize the triumph of good over evil.Dosmochey Festival
Approximate Time: Early February
Location: Leh, Diskit, Likir
Highlights: Known as the “Festival of the Scapegoat,” this festival involves rituals to ward off evil spirits.
Spring Festivals in Ladakh (March to May)
Spring brings color and renewal to Ladakh, celebrated through spiritual rituals and cultural performances.
Stok Guru Tsechu
Approximate Time: Late February to Early March
Location: Stok Monastery
Highlights: Lay oracle rituals and meditation-based spirit medium practices make this festival unique.Matho Nagrang Festival
Approximate Time: Early March
Location: Matho Monastery
Highlights: Monks in trance perform daring feats and offer prophecies, believed to reflect the year’s outlook.Saka Dawa
Approximate Time: Late May to Early June
Location: Across Ladakh
Highlights: Celebrates the birth, enlightenment, and death of Buddha with prayers and acts of charity.
Summer Festivals in Ladakh (June to August)
Summertime in Ladakh draws travelers to its grand monastic festivals and age-old rituals that honor cultural heritage.
Hemis Tsechu
Approximate Time: Mid to Late June
Location: Hemis Monastery
Highlights: This grand festival celebrates the birth of Guru Padmasambhava with captivating mask dances.Yuru Kabgyat Festival
Approximate Time: Early June
Location: Lamayuru Monastery
Highlights: Features Cham dances and prayers for world peace and prosperity.Phyang Tsedup Festival
Approximate Time: Early to Mid July
Location: Phyang Monastery
Highlights: Sacred Thangka displays and traditional dances highlight Buddhist teachings and values.
Autumn Festivals in Ladakh (September to November)
Autumn brings a serene yet colorful charm to Ladakh’s festivals, blending ritual and celebration in unique ways.
Diskit Gustor
Approximate Time: Late October
Location: Diskit Monastery
Highlights: Monks perform Cham dances that convey the victory of good forces over evil.Thiksey Gustor
Approximate Time: Mid to Late November
Location: Thiksey Monastery
Highlights: A two-day festival with masked dances, symbolizing spiritual victory and protection.Galdan Namchot
Approximate Time: Early December
Location: Throughout Ladakh
Highlights: Celebrates the birth of Tsongkhapa, a revered Tibetan Buddhist figure, marking preparations for Losar.
Sustainable Travel Tips for Ladakh
Sustainable Travel is something that should be implemented in the tourism industry worldwide. In return for all the good experiences we get from destinations like Ladakh, we have a responsibility to try to preserve this experience for the future generations. Our small actions like proper garbabe (specially plastic) disposal & supporting the local economy by buying local items can have an huge impact on the environment and local economy.
Consider the below Sustainable Travel Tips for your upcoming journey to Ladakh :
- Minimize Environmental Impact: Reduce plastic use by carrying reusable bottles and bags, avoid littering, and dispose of waste responsibly.
- Support Local Businesses: Stay in locally owned accommodations, eat at local restaurants, and buy souvenirs from local artisans.
- Responsible Tourism Practices: Respect the local culture and traditions, adhere to designated trails to prevent erosion, and conserve water.
FAQ’S About Ladakh Trip
- Travel Permits: Inner Line Permit (ILP) for Indian citizens and Protected Area Permit (PAP) for foreign nationals are required to visit certain areas.
- Altitude Sickness: Gradual acclimatization, staying hydrated, and avoiding alcohol can help prevent altitude sickness.
- Best Time to Visit: June to September for pleasant weather and accessibility, October to May for winter experiences.
- Local Transport: Rented bikes, cars, and public transport options are available for getting around Ladakh.
- Cultural Etiquette: Dress modestly, respect local customs, and follow monastery etiquette.
Contact Us for Personalized Stay & Transport Recommendations
Planning a trip to Ladakh and unsure where to stay or how to get around?
Contact us for any kind of guidance on accommodations and transport options tailored to your specific preferences and budget.
Whether you’re seeking a luxury resort, a cozy guesthouse, or a unique camping experience, our knowledgeable team can provide personalized recommendations to ensure you find the perfect place to stay.
We also assist with arranging reliable transport options, from private taxis to shared cabs, ensuring your travel in Ladakh is comfortable and hassle-free. You can fill the form below:
Ladakh Tour Packages
We hope you enjoyed reading this article and it will help you plan your next trip to Ladakh.
“May the spirit of the mountains guide you, and the peace of the valleys stay with you.”
Julley!

